Politics
Ronald Reagan: The Legacy of the 40th President of the United States

Ronald Reagan, the 40th president of the United States, is one of the most influential and transformative figures in modern American history. A former actor turned politician, Reagan’s presidency marked a dramatic shift in the political landscape, shaping the direction of the country for decades to come. Often referred to as “The Great Communicator,” Reagan was known for his charm, optimism, and ability to connect with Americans across the political spectrum.
This blog will explore Reagan’s life and career, from his humble beginnings to his years as a Hollywood actor, governor of California, and, finally, his two terms as president. We will examine the key moments of his presidency, his policies, and the lasting impact of the “Reagan Revolution” on both American politics and the world stage.
Early Life: From Humble Beginnings to Hollywood

Ronald Wilson Reagan was born on February 6, 1911, in Tampico, Illinois. Raised in a modest household, Reagan’s early years were shaped by his family’s financial struggles. His father, Jack Reagan, worked as a shoe salesman and struggled with alcoholism, while his mother, Nelle, was a devout Christian who instilled in her son a sense of optimism and faith.
Reagan attended Dixon High School, where he excelled in athletics and developed an interest in drama. After graduating, he attended Eureka College, where he studied economics and sociology and participated in student government and theater.
Upon graduating from college during the Great Depression, Reagan took a job as a radio announcer in Iowa, covering sports events. It wasn’t long before his distinctive voice and charismatic personality caught the attention of Hollywood talent scouts. In 1937, Reagan signed a contract with Warner Bros. and began his career as a film actor.
Hollywood Career: From B-Movies to the Big Screen
Ronald Reagan’s Hollywood career spanned nearly three decades, during which he appeared in over 50 films. While he never reached the level of stardom enjoyed by some of his contemporaries, Reagan found steady work in a variety of genres, including Westerns, dramas, and comedies.
One of his most notable roles came in the 1940 film Knute Rockne, All American, in which he portrayed the legendary football player George Gipp. His portrayal of Gipp earned him the nickname “The Gipper,” a moniker that would stick with him for the rest of his life.
Reagan’s acting career was interrupted by World War II, during which he served in the U.S. Army Air Forces. Due to his poor eyesight, he was assigned to a unit that produced training films for the military.
After the war, Reagan returned to Hollywood, but the film industry was changing, and his career began to decline. However, his time in the film industry provided him with valuable experience in public speaking and media, skills that would serve him well in his later political career.
Political Awakening: From Democrat to Conservative Leader
During the early years of his life, Ronald Reagan was a Democrat. He supported Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal policies and campaigned for Democratic candidates. However, by the 1950s, Reagan’s political views began to shift.
As president of the Screen Actors Guild, Reagan became deeply involved in labor disputes and the fight against communist influence in Hollywood. His experiences during this time, along with his growing opposition to government intervention in the economy, led him to embrace conservative principles.
By the early 1960s, Reagan had officially switched his political affiliation to the Republican Party. His 1964 speech, “A Time for Choosing,” delivered in support of Republican presidential candidate Barry Goldwater, catapulted Reagan into the national spotlight. In the speech, Reagan criticized government overreach and called for a return to individual responsibility and free-market principles. The speech resonated with conservatives across the country and set the stage for Reagan’s political rise.
Governor of California: A Test of Leadership
In 1966, Ronald Reagan ran for governor of California as a Republican, positioning himself as a champion of conservative values and a critic of the state’s liberal policies. Despite having no prior experience in elected office, Reagan won the election in a landslide, defeating incumbent Governor Pat Brown.
As governor, Reagan faced a series of challenges, including student protests at the University of California, Berkeley, rising crime rates, and a state budget deficit. He responded by implementing conservative policies, including tax cuts, welfare reform, and a crackdown on protests. While his tough stance on law and order won him praise from conservatives, it also drew criticism from liberal groups.
Reagan’s tenure as governor helped solidify his reputation as a strong, principled leader. He won re-election in 1970 and continued to push for conservative reforms. By the time he left office in 1975, Reagan was widely regarded as a leading figure in the Republican Party, and many believed it was only a matter of time before he ran for the presidency.
The Road to the White House: Reagan’s Presidential Campaigns
Ronald Reagan first ran for president in 1976, challenging incumbent Republican President Gerald Ford in the primaries. Although Reagan’s campaign gained significant momentum, he narrowly lost the nomination to Ford. However, the campaign had demonstrated Reagan’s broad appeal to conservative voters and positioned him as the front-runner for the 1980 election.
In 1980, Reagan ran for president again, this time securing the Republican nomination. His campaign was built around a message of reducing government interference in the economy, strengthening national defense, and restoring American pride. He also capitalized on the growing discontent with the presidency of Jimmy Carter, whose administration was struggling with high inflation, unemployment, and the Iran hostage crisis.
On November 4, 1980, Ronald Reagan won a decisive victory, defeating Carter in a landslide and becoming the 40th president of the United States.
The Reagan Revolution: Transforming American Politics
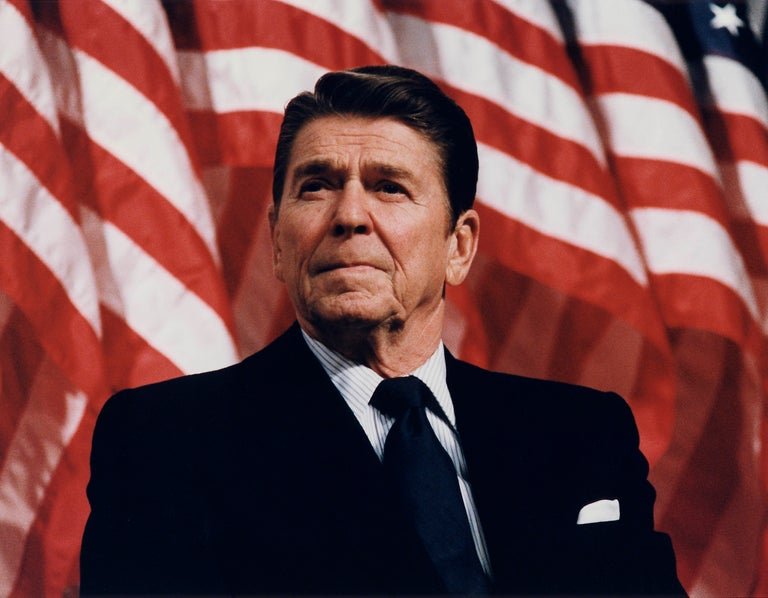

Ronald Reagan’s presidency is often described as a revolution—a dramatic shift in the direction of American politics. When he took office in January 1981, the country was facing a series of challenges, including economic stagnation, high inflation, and a declining sense of national pride. Reagan’s response was to implement a bold, conservative agenda that would come to define his presidency.
Economic Policy: Reaganomics
One of the central pillars of Reagan’s presidency was his economic policy, known as “Reaganomics.” The philosophy behind Reaganomics was based on supply-side economics, which argued that cutting taxes and reducing government regulation would stimulate economic growth.
Reagan’s administration implemented a series of tax cuts, including the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981, which reduced the top marginal tax rate from 70% to 50%. The goal was to give individuals and businesses more money to invest in the economy, leading to job creation and increased productivity.
At the same time, Reagan sought to reduce the size of the federal government by cutting spending on social programs. He believed that government intervention in the economy was part of the problem, not the solution, and that private enterprise was the key to economic growth.
While Reagan’s tax cuts and deregulation efforts were praised by conservatives, they also led to significant budget deficits, as government revenues declined faster than spending. Critics argued that Reaganomics disproportionately benefited the wealthy and increased income inequality. However, by the mid-1980s, the economy had rebounded, and Reagan’s supporters credited his policies with revitalizing the nation’s economy.
Foreign Policy: Confronting the Soviet Union
In addition to his domestic agenda, Ronald Reagan’s foreign policy was focused on confronting the Soviet Union and ending the Cold War. Early in his presidency, Reagan took a hardline stance against communism, referring to the Soviet Union as the “evil empire” and calling for an increase in U.S. military spending.
Reagan’s administration invested heavily in defense, including the development of new weapons systems and the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), a missile defense program that became known as “Star Wars.” While SDI was controversial and faced skepticism from both allies and adversaries, it signaled Reagan’s commitment to challenging Soviet power.
Reagan’s foreign policy also included support for anti-communist movements around the world. His administration provided aid to rebels fighting communist regimes in countries such as Afghanistan, Nicaragua, and Angola, as part of a broader effort to roll back Soviet influence.
The Reagan Doctrine: Spreading Freedom
The “Reagan Doctrine” became a cornerstone of U.S. foreign policy during Reagan’s presidency. The doctrine called for supporting freedom fighters and anti-communist movements in an effort to contain and eventually defeat the spread of communism. Reagan’s administration provided military and financial aid to resistance groups in various regions, including Central America, Africa, and Asia.
One of the most notable examples of the Reagan Doctrine in action was the U.S. support for the Mujahideen in Afghanistan, who were fighting Soviet forces after the Soviet invasion of the country in 1979. Reagan’s administration funneled significant aid to the Mujahideen, a strategy that helped drive the Soviets out of Afghanistan and ultimately contributed to the collapse of the Soviet Union.
The End of the Cold War: Negotiating Peace
While Reagan is often remembered for his tough rhetoric towards the Soviet Union, his presidency also saw a significant shift towards diplomacy, particularly during his second term. After years of confrontation, Reagan developed a close working relationship with Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev, who had come to power in 1985.
Gorbachev’s policies of glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) signaled a willingness to reform the Soviet system and reduce tensions with the West. Reagan saw an opportunity to negotiate and began a series of high-level talks with Gorbachev, resulting in several landmark agreements.
In 1987, Reagan and Gorbachev signed the Intermediate-Range Nuclear
Share this content:

Politics
Ronald Dion DeSantis: A Rising Political Figure

Ronald Dion DeSantis, often referred to simply as Ron DeSantis, is one of the most prominent figures in American politics today. As the 46th Governor of Florida, he has made headlines for his policies, leadership style, and national ambitions. From his military service to his growing influence in the Republican Party, DeSantis has positioned himself as a major player in the future of U.S. politics. This article delves into his background, achievements, controversies, and potential path toward a national stage.
Early Life and Education
Ron DeSantis was born on September 14, 1978, in Jacksonville, Florida, into a working-class family. Raised in Dunedin, Florida, DeSantis had a fairly traditional upbringing, excelling in both academics and athletics. He attended Dunedin High School, where he was known for his talent in baseball, a sport that would later play a significant role in his college years.
After high school, DeSantis attended Yale University, one of the most prestigious Ivy League schools in the country. While at Yale, he continued his passion for baseball, becoming the captain of the Yale Bulldogs baseball team. His academic prowess was equally impressive, earning a Bachelor of Arts degree in History, graduating with honors in 2001.
Following his time at Yale, DeSantis went on to attend Harvard Law School, where he earned a Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree in 2005. His academic background from these two elite institutions would later help solidify his credentials as a rising political star.
Military Service
DeSantis’s journey into public service began with his military career. Shortly after graduating from Harvard Law School, he was commissioned as an officer in the United States Navy’s Judge Advocate General’s Corps (JAG). His role as a military lawyer took him to several key assignments, including working with the U.S. Navy SEALs.
One of the most notable moments of DeSantis’s military career came in 2007 when he was deployed to Iraq as part of the U.S. Navy SEALs’ legal team. He served as a legal advisor during the surge in Iraq, a critical time when the U.S. military was working to combat insurgent forces. DeSantis earned several commendations for his service, including the Bronze Star Medal for meritorious service.
His military experience has often been highlighted in his political career, emphasizing his dedication to service and leadership in challenging circumstances. It also played a role in shaping his foreign policy views, particularly his strong stance on national security and support for veterans.
Early Political Career

After returning from his military service, DeSantis transitioned into a career in politics. In 2012, he ran for a seat in the U.S. House of Representatives in Florida’s 6th congressional district. DeSantis’s campaign was built on a platform of fiscal conservatism, limited government, and a commitment to constitutional principles.
DeSantis won the election and served three terms in Congress from 2013 to 2018. During his time in the House of Representatives, he quickly gained a reputation as a staunch conservative. He aligned himself with the Tea Party movement and was a member of the House Freedom Caucus, a group of conservative lawmakers dedicated to promoting limited government and reducing federal spending.
One of DeSantis’s notable legislative efforts was his work on military and veteran affairs. Given his own background in the military, he championed policies aimed at improving healthcare services for veterans and ensuring that the military remained well-funded and prepared for emerging global threats.
The Road to the Governorship
DeSantis’s congressional career laid the foundation for his next major political move: running for governor of Florida. In 2018, he announced his candidacy for the Republican nomination for Governor of Florida, a race that would become one of the most closely watched in the nation.
One of the key factors in DeSantis’s rise to prominence during the gubernatorial race was his endorsement by then-President Donald Trump. Trump’s support helped DeSantis win the Republican primary, where he faced off against Agriculture Commissioner Adam Putnam. DeSantis’s victory in the primary was seen as a major upset, as Putnam had been considered the favorite for much of the race.
In the general election, DeSantis faced Democrat Andrew Gillum, the mayor of Tallahassee. The race was intensely competitive and closely divided, with national attention focused on Florida as a battleground state. DeSantis ultimately won the election by a narrow margin, securing 49.6% of the vote to Gillum’s 49.2%.
Policies and Leadership as Governor
Since taking office in January 2019, DeSantis has implemented a range of policies that have defined his tenure as Governor of Florida. His administration has been marked by a focus on conservative values, economic growth, and a hands-off approach to governance. However, his leadership style has also sparked controversy, particularly in the areas of public health, education, and civil rights.
COVID-19 Response
One of the most defining moments of DeSantis’s governorship has been his handling of the COVID-19 pandemic. Florida, as one of the largest and most populous states in the country, was a focal point in the national conversation about pandemic response.
DeSantis took a notably different approach from many other governors, particularly in Democratic-led states. He resisted calls for prolonged lockdowns and was one of the first governors to reopen the state’s economy, emphasizing personal freedom and the need to keep businesses operational. DeSantis also opposed mask mandates and vaccine passports, arguing that such measures infringed on individual liberties.
While his approach was praised by many conservatives and business owners who supported reopening efforts, it was met with sharp criticism from public health officials and Democrats. Critics argued that his policies led to higher infection rates and unnecessary deaths, particularly among vulnerable populations. Nonetheless, DeSantis’s response to the pandemic solidified his reputation as a champion of individual freedoms and limited government intervention.
Education
Education has been another major area of focus for DeSantis. He has pushed for reforms aimed at expanding school choice, increasing funding for charter schools, and limiting what he sees as ideological indoctrination in public education. One of his most controversial moves was his support for the “Stop WOKE Act,” a piece of legislation aimed at restricting how race and history are taught in Florida schools.
The act, which bans the teaching of certain concepts related to critical race theory, has been praised by conservatives who argue that it prevents the politicization of education. However, it has been fiercely opposed by teachers’ unions, civil rights groups, and many educators who believe it stifles free speech and limits the ability to discuss important aspects of American history.
Environment
Despite his conservative credentials, DeSantis has made efforts to address environmental issues in Florida, particularly regarding water quality and Everglades restoration. Early in his governorship, he signed a series of executive orders aimed at improving water quality in the state and tackling the issue of red tide, a harmful algal bloom that has affected Florida’s coastline.
DeSantis has also supported efforts to protect the Everglades, securing significant funding for restoration projects aimed at preserving the state’s unique ecosystem. His environmental policies have earned him praise from some conservation groups, though critics argue that his overall environmental record is mixed, particularly in his support for deregulation that some say harms long-term sustainability.
National Ambitions
As DeSantis’s profile has risen, so too has speculation about his national political ambitions. Many see him as a potential presidential candidate, particularly given his strong alignment with the conservative base of the Republican Party. His handling of the COVID-19 pandemic and his willingness to take on “woke” culture have made him a favorite among Republicans who are looking for a successor to Donald Trump.
DeSantis’s relationship with Trump is an interesting dynamic in itself. While Trump’s endorsement was crucial to DeSantis’s success in the 2018 gubernatorial race, there have been signs of tension between the two as DeSantis’s national profile has grown. Some political observers believe that DeSantis may seek to challenge Trump for the Republican nomination in the 2024 presidential election, should Trump decide to run again.
Regardless of whether DeSantis runs for president in 2024, his influence within the Republican Party is undeniable. He has become a key figure in shaping the party’s future, particularly in terms of its stance on issues like government regulation, individual freedoms, and cultural conservatism.
Controversies and Criticism
Like many high-profile political figures, DeSantis has not been without controversy. His handling of the COVID-19 pandemic, his stance on education, and his aggressive approach to culture wars have drawn sharp criticism from Democrats, public health experts, and civil rights advocates.
One of the most significant criticisms of DeSantis has been his perceived prioritization of political considerations over public health during the pandemic. Critics argue that his refusal to impose mask mandates and his opposition to vaccine requirements contributed to the spread of the virus and put vulnerable populations at risk. DeSantis, however, has consistently defended his approach, arguing that it was necessary to protect individual liberties and prevent economic collapse.
Another area of controversy has been DeSantis’s approach to education. His support for laws limiting the teaching of certain racial and historical topics has sparked widespread debate about academic freedom and the role of government in shaping school curricula. Supporters argue that these measures are necessary to prevent ideological indoctrination, while opponents see them as an infringement on free speech and an attempt to whitewash American history.
Conclusion
Ronald Dion DeSantis is a complex and influential figure in modern American politics. As Governor of Florida, he has championed conservative policies, focusing on individual freedom, limited government intervention, and cultural conservatism. His leadership during the COVID-19 pandemic and his stances on education and environmental issues have defined his governorship and earned him both
Share this content:
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoВетеринарная клиника VetCityPets: Забота о вашем питомце на высшем уровне
-
 App6 months ago
App6 months agoExperience Unlimited Entertainment with Castle APK for Android
-

 Business8 months ago
Business8 months agoSnow Day Calculator: How to Predict School Closures
-

 AI8 months ago
AI8 months agoUnderstanding 라마 3.1: Features, Benefits, and Applications
-

 Business7 months ago
Business7 months agoLand Rover Defender vs. Toyota Land Cruiser: Battle of the Luxury Off-Roaders
-

 Travel6 months ago
Travel6 months agoExplore Mega-Personal.net Travel Archives: Your Gateway
-
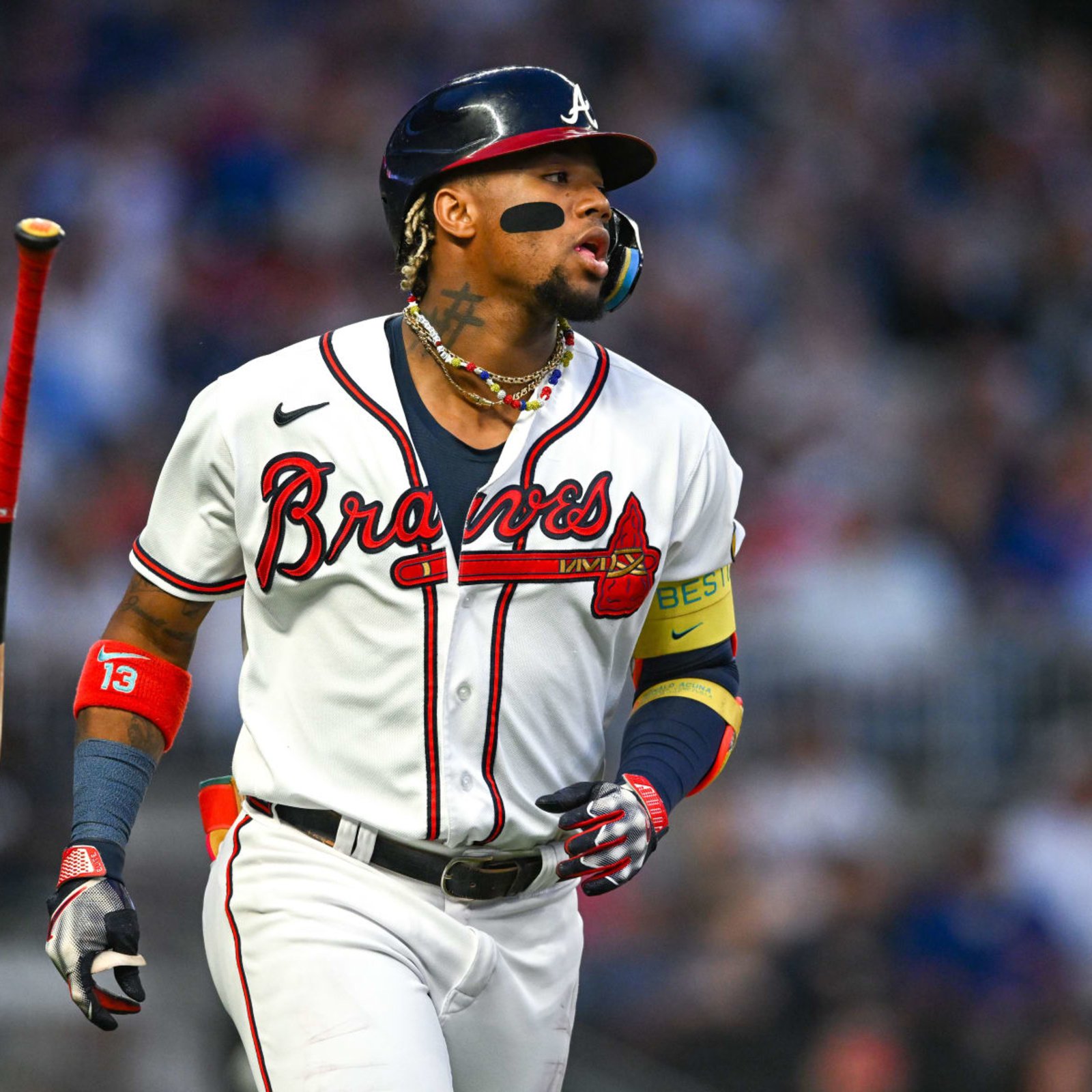

 Ronaldo8 months ago
Ronaldo8 months agoRonald Acuña Jr.: The Rise of a Baseball Superstar
-

 BLOG8 months ago
BLOG8 months agoThe Ultimate Guide to Becoming a Car Guru: Tips for Car Enthusiasts and Buyers