News
Tesla: Revolutionizing the Automotive Industry with Innovation and Sustainability

Introduction
Tesla, Inc., founded in 2003, has dramatically transformed the automotive industry. Known for its electric vehicles (EVs), energy solutions, and advancements in autonomous driving, Tesla has become synonymous with innovation and sustainability. This blog dives into the company’s history, product range, and impact on the world of automotive technology.
Table of Contents
1. The Origins of Tesla
2. Tesla’s Mission and Vision
3. The Tesla Lineup: A Look at the Cars
4. Autopilot and Full Self-Driving: Redefining Autonomous Driving
5. Tesla Energy and the Path to a Sustainable Future
6. The Tesla Gigafactories: Scaling Production and Innovation
7. The Impact of Tesla on the EV Market
8. Future Prospects and Challenges for Tesla
9. Conclusion
10. FAQs
1. The Origins of Tesla
Tesla was founded in 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, with Elon Musk joining shortly after as an investor and chairman. The company aimed to prove that electric vehicles could be better, faster, and more enjoyable than traditional gas-powered cars. From the start, Tesla’s vision was ambitious—developing EVs that would reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote renewable energy.
2. Tesla’s Mission and Vision
Tesla’s mission, “to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy,” captures its core goal. Tesla is focused on creating products and technologies that enable cleaner energy use, making sustainability more accessible to consumers. Tesla’s commitment to sustainability isn’t just in its cars but also in its energy solutions, like solar panels and energy storage systems.
3. The Tesla Lineup: A Look at the Cars
Tesla’s vehicle lineup has expanded over the years to cater to different market segments. Here’s a breakdown:
Tesla Roadster: Tesla’s first production vehicle, the Roadster, was a high-performance sports car that demonstrated the potential of electric cars. Its 2008 release marked a significant shift in public perception about EVs.
Model S: The Model S, launched in 2012, brought luxury and performance together in an EV sedan. With cutting-edge features, the Model S achieved a high range and impressive acceleration, making it a benchmark in the EV market.
Model X: Known for its distinctive falcon-wing doors, the Model X SUV combines luxury with practicality. It offers ample space, an all-wheel-drive option, and the same impressive performance characteristics Tesla is known for.
Model 3: The Model 3 sedan made Tesla’s vision of sustainable transportation accessible to a broader audience. With a more affordable price, it quickly became one of the best-selling EVs in the world.
Model Y: Introduced in 2020, the Model Y compact SUV offers versatility and functionality with similar specs to the Model 3. It caters to the growing demand for SUVs without sacrificing Tesla’s iconic performance.
Each Tesla model is equipped with unique features like high battery ranges, a minimalist interior with a central touchscreen, and advanced software.
4. Autopilot and Full Self-Driving: Redefining Autonomous Driving
Tesla’s Autopilot system is one of its most talked-about features. It uses a suite of sensors and cameras to enable semi-autonomous driving capabilities, allowing the car to steer, accelerate, and brake automatically in certain conditions. Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) package promises even greater autonomy, including features like:
Automatic Lane Changes: Assists in safe lane changes on highways.
Autonomous Navigation: Allows the vehicle to navigate to destinations without driver input.
Traffic Light and Stop Sign Recognition: Enables the car to recognize and respond to traffic signals.
Tesla aims to achieve full Level 5 autonomy, which would make its vehicles capable of driving independently in any environment. However, the technology and regulations still need to catch up.
5. Tesla Energy and the Path to a Sustainable Future

Tesla isn’t just a car manufacturer; it’s an energy company. Tesla Energy focuses on products that support sustainable energy generation and storage, such as:
Solar Panels and Solar Roof: Tesla’s solar solutions convert sunlight into energy for homes, reducing dependence on the grid.
Powerwall and Powerpack: These are Tesla’s battery storage systems for residential and commercial use, storing excess energy generated by solar panels.
Tesla’s energy products integrate with each other and can be managed through the Tesla app. This ecosystem supports Tesla’s vision of a sustainable energy future, where households and businesses can rely on renewable energy without interruptions.
6. The Tesla Gigafactories: Scaling Production and Innovation
To meet the increasing demand for EVs and energy products, Tesla has established several Gigafactories worldwide. These facilities are more than just production plants; they represent Tesla’s commitment to sustainability and innovation. Here’s a look at some of the most notable ones:
Gigafactory Nevada: The first Gigafactory, focused on producing batteries and powertrains, helping Tesla lower costs and increase battery production.
Gigafactory Shanghai: Tesla’s first factory outside the U.S., which has allowed Tesla to tap into the Chinese market while reducing production costs.
Gigafactory Berlin: Currently under construction, it’s Tesla’s first European Gigafactory, set to produce the Model Y and battery cells for European markets.
Gigafactory Texas: This is one of Tesla’s most ambitious projects, aiming to produce the Model Y, Cybertruck, and Tesla Semi.
7. The Impact of Tesla on the EV Market
Tesla has not only increased the popularity of EVs but also set a high standard for performance, technology, and sustainability. Several impacts include:
Influencing Traditional Automakers: Major car manufacturers have been compelled to accelerate their EV programs to compete with Tesla.
Advancing Battery Technology: Tesla’s focus on battery technology has led to breakthroughs in battery efficiency and longevity.
Shifting Public Perception: Tesla’s success has proven that EVs can be high-performing, stylish, and sustainable.
8. Future Prospects and Challenges for Tesla
Tesla’s future is filled with exciting possibilities and significant challenges:
Cybertruck: Tesla’s upcoming electric truck has generated immense interest. Its unconventional design and high durability promise to make it a game-changer in the pickup truck market.
Tesla Semi: This electric truck aims to revolutionize the logistics industry with zero-emission transportation and lower operational costs.
Tesla Robot: Tesla is developing an AI-powered robot, expanding its reach beyond automotive and energy industries.
Challenges Tesla faces include increasing competition, regulatory hurdles, and technological limitations, particularly in achieving full autonomy.
Conclusion
Tesla has grown from a small startup to a global leader in sustainable transportation and energy solutions. By pioneering advancements in EVs, battery technology, and autonomous driving, Tesla has reshaped the automotive industry. Its commitment to sustainability and innovation continues to inspire both consumers and competitors alike.
FAQs
What is Tesla’s main goal?
Tesla’s mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
What cars does Tesla offer?
Tesla currently offers the Model S, Model X, Model 3, Model Y, and has announced the Cybertruck and Tesla Semi.
Is Tesla’s Autopilot fully autonomous?
Not yet. Tesla’s Autopilot provides semi-autonomous features, but full autonomy is still in development.
What is Tesla Energy?
Tesla Energy offers sustainable energy solutions like solar panels, the Powerwall, and the Powerpack, which allow energy generation and storage for homes and businesses.
What are Tesla’s Gigafactories?
Gigafactories are Tesla’s large-scale production facilities for EV batteries, vehicles, and energy products.
Share this content:
News
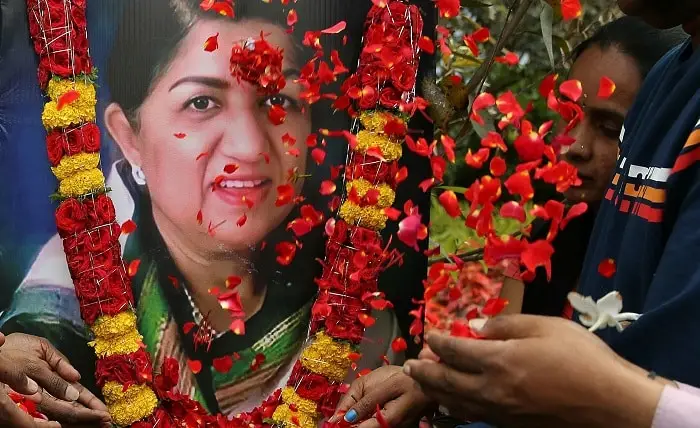
Remembering Lata Mangeshkar: The Nightingale of India

Lata Mangeshkar, fondly known as the “Nightingale of India,” was more than just a singer—she was the voice of a nation. Born on September 28, 1929, in Indore, her unparalleled career spanned eight decades. With her ethereal voice, she captured the hearts of millions and became an enduring symbol of India’s cultural heritage. Her untimely demise on February 6, 2022, marked the end of an era, leaving an irreplaceable void in the world of music.
Early Life and Journey Into Music
Lata Mangeshkar’s tryst with music began at an early age. She was the eldest of five siblings, and her father, Pandit Deenanath Mangeshkar, a classical singer, played a pivotal role in nurturing her talent. Following his untimely death, Lata took up singing to support her family, starting with small roles in films.
Her first breakthrough came in 1949 with the song Aayega Aanewala from the movie Mahal. This marked the beginning of her rise as a playback singer in Bollywood, a journey that would redefine Indian music forever.
A Prolific Career

Over her illustrious career, Lata Mangeshkar lent her voice to over 30,000 songs in more than 36 languages, including Hindi, Marathi, Bengali, Tamil, and Urdu. Her melodious voice became synonymous with Indian cinema. Whether it was romantic ballads, devotional hymns, or patriotic anthems, her versatility was unmatched.
Milestone Songs:
“Ae Mere Watan Ke Logon”: A patriotic masterpiece that moved a nation to tears.
“Lag Ja Gale”: A hauntingly beautiful melody that remains a favorite across generations.
“Tere Bina Zindagi Se”: A poignant duet with Kishore Kumar that showcased her emotive depth.
She collaborated with legendary music directors like S.D. Burman, R.D. Burman, and Madan Mohan, creating timeless classics that continue to resonate with audiences.
Honors and Awards
Lata Mangeshkar was the recipient of numerous accolades, reflecting her monumental contributions to music. Some of her most notable honors include:
Bharat Ratna (2001): India’s highest civilian award.
Padma Bhushan (1969) and Padma Vibhushan (1999).
Dadasaheb Phalke Award (1989): The highest recognition in Indian cinema.
Multiple Filmfare Awards and National Film Awards.
Her achievements were not just limited to India. Her voice transcended borders, earning her international recognition and adoration.
The Final Days
In January 2022, Lata Mangeshkar was hospitalized after contracting COVID-19. Despite initial signs of recovery, complications arose, leading to her passing due to multiple organ failure. She left us on February 6, 2022, at the age of 92, leaving an entire nation in mourning.
A Nation’s Tribute

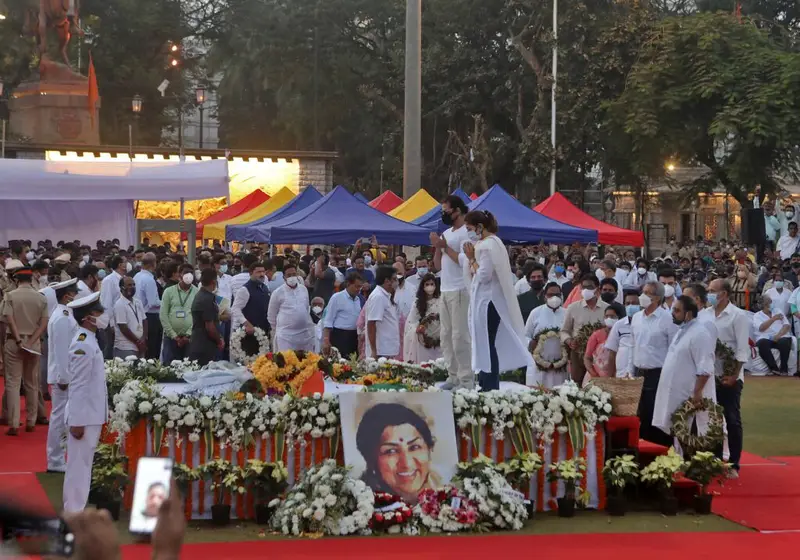
The Government of India declared two days of national mourning to honor her memory, with flags flying at half-mast. Leaders, celebrities, and fans from across the globe paid heartfelt tributes. Prime Minister Narendra Modi described her passing as “an irreparable loss to the nation.”
Her funeral at Mumbai’s Shivaji Park was conducted with full state honors. Thousands gathered to bid farewell, a testament to the profound impact she had on people’s lives.
Legacy
Lata Mangeshkar’s voice will forever echo in the hearts of millions. Her songs remain timeless, a part of India’s cultural fabric. Beyond her musical genius, she inspired generations of artists, setting a benchmark for excellence and humility.
As we remember her, we celebrate a life dedicated to the pursuit of artistic perfection. Lata Mangeshkar was not just a singer; she was the soul of India’s music, and her legacy will continue to inspire for generations to come.

Conclusion
Lata Mangeshkar’s passing marked the end of an era, but her legacy endures. Her voice, filled with emotion and grace, remains a source of solace and joy. She may no longer be with us, but her songs will continue to light up our lives.
FAQs
1. Why is Lata Mangeshkar called the “Nightingale of India”?
Lata Mangeshkar earned this title due to her melodious and soulful voice, which captivated audiences and became an integral part of Indian music.
2. How many songs did Lata Mangeshkar sing?
She recorded over 30,000 songs in more than 36 languages, making her one of the most prolific singers in the world.
3. What are Lata Mangeshkar’s most famous songs?
Some of her iconic songs include Ae Mere Watan Ke Logon, Lag Ja Gale, and Tere Bina Zindagi Se.
4. What awards did Lata Mangeshkar receive?
She was honored with numerous awards, including the Bharat Ratna, Padma Bhushan, and Dadasaheb Phalke Award.
5. What is Lata Mangeshkar’s legacy?
Her legacy is one of timeless music, unparalleled dedication, and inspiration for countless artists worldwide.
Share this content:
News
Elon Musk Pays $11 Billion in Taxes: What It Means Billionaires

Introduction
In 2021, Elon Musk, the world-renowned billionaire entrepreneur and CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, made headlines for paying a staggering $11 billion in taxes. This event sparked intense debates about wealth, taxation, and the responsibilities of the ultra-wealthy in contributing to societal development. The keyword “www.rajkotupdates.news : elon musk pay 11 billion in taxes” has been trending due to widespread curiosity about how this massive tax payment came about and its implications. In this blog, we’ll break down the reasons behind this tax payment, its impact, and the broader conversation about tax policies for billionaires.
Why Did Elon Musk Pay $11 Billion in Taxes?
Elon Musk’s tax payment in 2021 was primarily driven by the following factors:
1. Stock Sales
Musk sold a significant portion of Tesla shares to cover the tax liability arising from exercising stock options. These stock options, granted as part of his compensation package, were nearing their expiration date, prompting him to convert them into shares.
2. Capital Gains Tax
The U.S. tax system requires individuals to pay taxes on capital gains when stocks are sold. Since Musk’s Tesla shares had significantly appreciated in value, his tax bill was proportionately high.
3. Wealth Increase
Musk’s net worth skyrocketed in recent years, making him the world’s richest person at the time. This exponential increase in wealth attracted attention to how much taxes billionaires like him actually pay.
4. Public Pressure
Public scrutiny regarding billionaire taxation played a role in Musk’s decision to publicize his massive tax payment, showcasing his compliance with tax obligations.
How Does $11 Billion Compare?
To put Musk’s $11 billion tax payment into perspective:
It is the largest single-year tax payment ever made by an individual in U.S. history.
This amount is equivalent to the annual budget of some small countries.
Despite the massive payment, it constitutes a small fraction of Musk’s overall net worth, which exceeded $200 billion at the time.
The Debate Around Billionaire Taxes
Musk’s tax payment reignited debates about taxation policies for billionaires. Here are some key arguments for and against higher taxes on the wealthy:
Arguments in Favor of Higher Taxes
1. Fair Contribution
Billionaires often grow their wealth exponentially due to stock appreciation and other investments. Advocates argue that they should contribute proportionately to society.
2. Funding Social Programs
Higher taxes on the ultra-wealthy can be used to fund essential programs like healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
3. Closing Wealth Inequality
The wealth gap between billionaires and the average citizen has widened. Increased taxation could help bridge this gap.
Arguments Against Higher Taxes
1. Discouraging Innovation
Critics argue that excessive taxation may discourage entrepreneurs from taking risks and investing in innovation.
2. Job Creation
Many billionaires, including Musk, argue that their companies create jobs and economic growth, which indirectly benefits society.
3. Global Competition
Higher taxes in one country may prompt billionaires to relocate to nations with lower tax rates, potentially harming the local economy.
Elon Musk’s Views on Taxes
Elon Musk has been vocal about his opinions on taxation. While he supports paying his fair share, he has criticized what he perceives as unfair tax policies. Musk has pointed out that he does not receive a salary from Tesla or SpaceX, relying instead on stock options for income. He has also argued that a significant portion of his wealth is reinvested in ventures like space exploration and renewable energy, benefiting humanity at large.
Impact of Elon Musk’s $11 Billion Tax Payment

Musk’s tax payment has had several ripple effects:
1. Increased Awareness
It has drawn attention to how much the ultra-wealthy pay in taxes and sparked calls for greater transparency in taxation.
2. Policy Discussions
The payment reignited debates about implementing a “wealth tax” or other reforms to ensure billionaires contribute more.
3. Philanthropy vs. Taxes
Many argue whether billionaires should focus on paying taxes or contributing directly to society through philanthropy.
4. Public Relations
Musk’s announcement of his tax payment helped counter criticism that billionaires avoid taxes.
Billionaire Taxation: The Road Ahead
The conversation around billionaire taxation is far from over. Governments worldwide are considering measures like:
Wealth Taxes
Taxes on net worth rather than income, ensuring billionaires pay more proportionately.
Closing Loopholes
Ensuring the wealthy cannot exploit tax loopholes to minimize liabilities.
Global Minimum Tax
Coordinating international efforts to prevent tax evasion through offshore accounts.
Public Reactions
Musk’s tax payment received mixed reactions:
Supporters applauded him for fulfilling his tax obligations and setting a precedent for other billionaires.
Critics argued that this was merely a fraction of his wealth and called for systemic changes to taxation policies.
Social media platforms, including www.rajkotupdates.news, saw a surge in discussions, with many users debating the fairness of current tax systems.
Conclusion
Elon Musk’s $11 billion tax payment is a landmark event, highlighting both the contributions and the controversies surrounding billionaire taxation. While it demonstrates compliance with existing tax laws, it also underscores the need for systemic reforms to address wealth inequality and ensure fair contributions from the ultra-wealthy.
The debate around taxation policies for billionaires will continue to evolve, shaping how societies balance innovation, wealth distribution, and economic growth. For now, Musk’s tax payment serves as a reminder of the immense financial responsibilities that come with immense wealth.
Share this content:
News
Remembering [Principal’s Name]: Celebrating the Legacy of Argyle Middle School’s Beloved Principal

Introduction
Announce the unfortunate passing of Argyle Middle Schools principal died.
Mention the impact of their leadership and dedication to the school community.
Introduce the main points of the article, which will cover their legacy, impact, and ways the community can honor their memory.
Main Sections
1. A Life Dedicated to Education and Community
Background and Career Highlights: Provide a brief history of the principal’s career, including how long they served at Argyle Middle School and any previous roles in education.
Values and Leadership Style: Describe the principal’s leadership qualities, such as compassion, dedication, and commitment to student success.
2. Their Impact on Argyle Middle School
Educational Initiatives: Highlight specific programs or initiatives the principal introduced to improve the educational experience.
Student Support: Describe any extra efforts made to support students’ academic, social, and emotional growth.
Community Engagement: Share stories of how the principal built connections with families, attended events, or created a welcoming environment for all.
3. Memories from Staff, Students, and Parents
Quotes and Tributes: Include memories from teachers, students, and parents, sharing how the principal impacted their lives.
Personal Anecdotes: If possible, add personal stories that illustrate their positive influence, like memorable speeches, favorite school traditions they led, or moments that brought the community together.
4. Supporting the School Community Through Grief
Grief Resources: Provide information on grief counseling or support services available to students, parents, and staff members.
Encouraging Open Conversations: Offer advice for parents and teachers on how to discuss grief with children in age-appropriate ways.
Remembering Together: Suggest holding a memorial event at the school, where students and staff can celebrate the principal’s life and share memories.
5. The Legacy They Leave Behind

Long-Term Impact: Discuss how the principal’s values and initiatives will continue to shape the school’s future.
Scholarships or Programs in Their Name: If applicable, mention any new scholarships or programs created in their honor to support students.
Inspiring Future Leaders: Encourage students to honor the principal’s legacy by embodying qualities they admired, such as kindness, perseverance, or commitment to learning.
6. How the Community Can Pay Tribute
Fundraisers or Donations: Share information on any memorial funds or charitable donations organized in their name.
Volunteer Opportunities: Encourage the community to honor their legacy by volunteering at the school or in related educational programs.
Creating a Memorial: Suggest a tribute, like a commemorative garden, plaque, or annual event, to keep their memory alive within the school.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
What Happened to [Principal’s Name]?
Provide a brief, respectful summary of their passing.
How Can We Support the School?
Mention ways to offer support, including donations or volunteering.
Will There Be a Memorial Service?
Share details on any scheduled memorial or gathering for the community.
Are There Resources for Grieving Students?
Reiterate the available grief resources and counseling options for students and staff.
What Legacy Did the Principal Leave?
Summarize the principal’s key contributions and lasting impact on Argyle Middle School.
Conclusion
Reaffirm the importance of remembering and honoring the principal’s legacy.
Encourage the Argyle Middle School community to come together in support of one another.
End with a heartfelt call to celebrate the life of a beloved principal who left a lasting, positive mark on everyone they met.
Share this content:
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoВетеринарная клиника VetCityPets: Забота о вашем питомце на высшем уровне
-

 Business7 months ago
Business7 months agoSnow Day Calculator: How to Predict School Closures
-
 App5 months ago
App5 months agoExperience Unlimited Entertainment with Castle APK for Android
-

 Ronaldo7 months ago
Ronaldo7 months agoRonald Acuña Jr.: The Rise of a Baseball Superstar
-

 BLOG7 months ago
BLOG7 months agoThe Ultimate Guide to Becoming a Car Guru: Tips for Car Enthusiasts and Buyers
-

 AI7 months ago
AI7 months agoUnderstanding 라마 3.1: Features, Benefits, and Applications
-

 Travel6 months ago
Travel6 months agoExplore Mega-Personal.net Travel Archives: Your Gateway
-

 Business6 months ago
Business6 months agoLand Rover Defender vs. Toyota Land Cruiser: Battle of the Luxury Off-Roaders





Pingback: The 2024 Tesla Cybertruck and Cyberbeast: A New Era of Electric Trucks - Ronaldo